Customizing VisiData
For a primer on configuring VisiData through setting options, see jsvine's tutorial.
How to configure commands
The .visidatarc in the user's home directory is plain Python code, and can contain additional commands or key bindings.
(Alternatively, since v2.9, VisiData has XDG support. If $XDG_CONFIG_HOME is set and the file "$XDG_CONFIG_HOME"/visidata/config.py exists, this will be loaded as the user's default configuration file.)
Longnames are names given to executable commands for ease of keystroke remapping. For example, the longname select-row is assigned to commands which select the current row in a sheet. On default, this longname is bound to the keystroke s.
From within VisiData, type z Ctrl+H to open the Commands Sheet. This is a reference for all of the commands available on the current sheet. For a deeper exploration of commands, check out API reference manual.
Setting/changing keybindings for existing commands
- Learn the longname for a command. Longnames are usually 2-3 words, separated by hyphens. The first word is usually a verb, and the second usually a noun. When a command is executed, its longname appears in the lower right status, next to its keystroke. Alternatively, you can
z Ctrl+Hto open the Commands Sheet and discover the longname for the command in question.
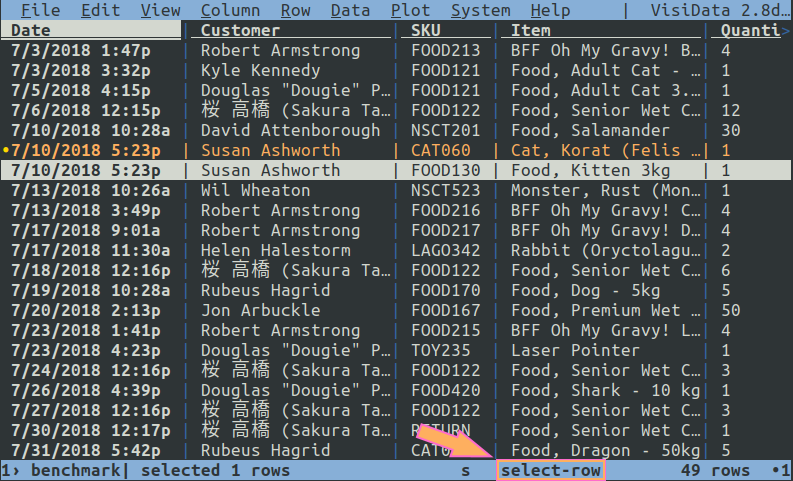
- a) To create a global keybinding, add
bindkey(keystroke, longname)to your .visidatarc.
b) To set the binding for a particular sheet type, add <Sheet>.bindkey(keystroke, longname) to your .visidatarc, where <Sheet> is a SheetType.
Warning: bindings defined in a .visidatarc will overwrite default ones.Example: Bind i to edit-cell globally
In VisiData, pressing e enters edit mode for the current cell. Seasoned vim users might prefer to press i instead.
- Open
~/.visidatarcin an editor. - Add the line
TableSheet.bindkey('i', 'edit-cell')to globally bind the keystrokeito the longnameedit-cell. - Launch VisiData, and press
i.
Example: Unbind i from addcol-incr globally
If the above instructions are followed, a message will pop up that says "i was already bound to addcol-incr.
To unbind i before binding it:
- Open
~/.visidatarcin an editor. - Add the line
TableSheet.unbindkey('i')before any piece of code where it is re-bound. - Launch VisiData.
Creating new commands
At minimum, <Sheet>.addCommand requires a longname and execstr.
For example, to define a new command:
Sheet.addCommand('^D', 'scroll-halfpage-down', 'cursorDown(nScreenRows//2); sheet.topRowIndex += nScreenRows//2')Commands and keybindings are set on a particular Sheet Type in the class hierarchy. Use BaseSheet for commands which don't need a sheet at all--these will apply to all sheets. Commands and bindings on more specific sheets will override more generic ones. Sheet is a generic table, ColumnsSheet would be for the columns sheet, FreqTableSheet for frequency tables, and so on.
Adding custom aggregators
Aggregators allow you to gather the rows within a single column, and interpret them using descriptive statistics. VisiData comes pre-loaded with a default set like mean, stdev, and sum.
To add your own custom aggregator name, add the following to your .visidatarc.
vd.aggregator('name', func, type=float)
Where func is a function of the form:
def func(list): return value
The type parameter is optional. It allows you to define the default type of the aggregated column.
Here is an example, that adds an aggregator for numpy's internal rate of return module.
import numpy as np vd.aggregator('irr', np.irr, type=float)
Bonus: How to choose which aggregators are columns within the DescribeSheet?
Any numeric aggregator can be added!
Supply a space-separated list of aggregator names to options.describe_aggrs in your .visidatarc.
options.describe_aggrs = 'mean stdev irr'
Turning off motd
By default, the first time each day that VisiData is used, it downloads a single small file of startup messages.
This network request can be turned off by adding options.motd_url='' to your ~/.visidatarc.
If you do decide to turn it off, we encourage you to donate to support VisiData.
